A few months back we reported that Google had put a special co-processing chip inside its new Pixel 2 and Pixel 2 XL phones but hadn’t turned it on.
Well, Google has now turned on the chip via a new software update with the immediate benefit being the improvement of image quality in third-party apps that enable you to take photos.
Google is talking about Instagram, WhatsApp, and Snapchat specifically, but there are of course many other apps that use the Pixel 2 camera; these new features are available to any app.
What's a co-processor?
Co-processors are essentially extra silicon inside a handset that facilitates specific functions – in the Pixel 2 and Pixel 2 XL the co-processor is to bring more intelligence to photo processing and aid machine learning which is behind the Pixel’s HDR+ technology.
The new Galaxy S9 will reportedly feature a Samsung-designed neural engine, while neural engines are also part of the latest Huawei and Apple devices, too. A co-processor is essentially like a scaled-back version of main mobile processors, orientated towards a specific purpose.
On Apple devices, there’s also an M co-processor (the latest of which is the M11) designed to process the sensor data from the accelerometer, gyroscope and compass so the main, thirstier CPU isn’t having to do the work and so reducing power consumption.
Google says its co-processor is "designed from scratch to deliver maximum performance at low power". Again, it’s power frugality that’s the name of the game here. Google says the Visual Core processing is five times faster than the Pixel 2's main CPU can do, but it uses a tenth of the energy.
Often the M co-processors are used is for fitness aps that need to work out what type of activity you’re are undertaking even when the phone is idle.
What's inside Google Pixel Core?
Software processing has thus far been behind the Pixel 2’s photo prowess, but it’s now received a significant power-up via Pixel Core.
It's become clear that Google worked with Intel on Pixel Core, but it's the first mobile silicon that Google has essentially designed itself.
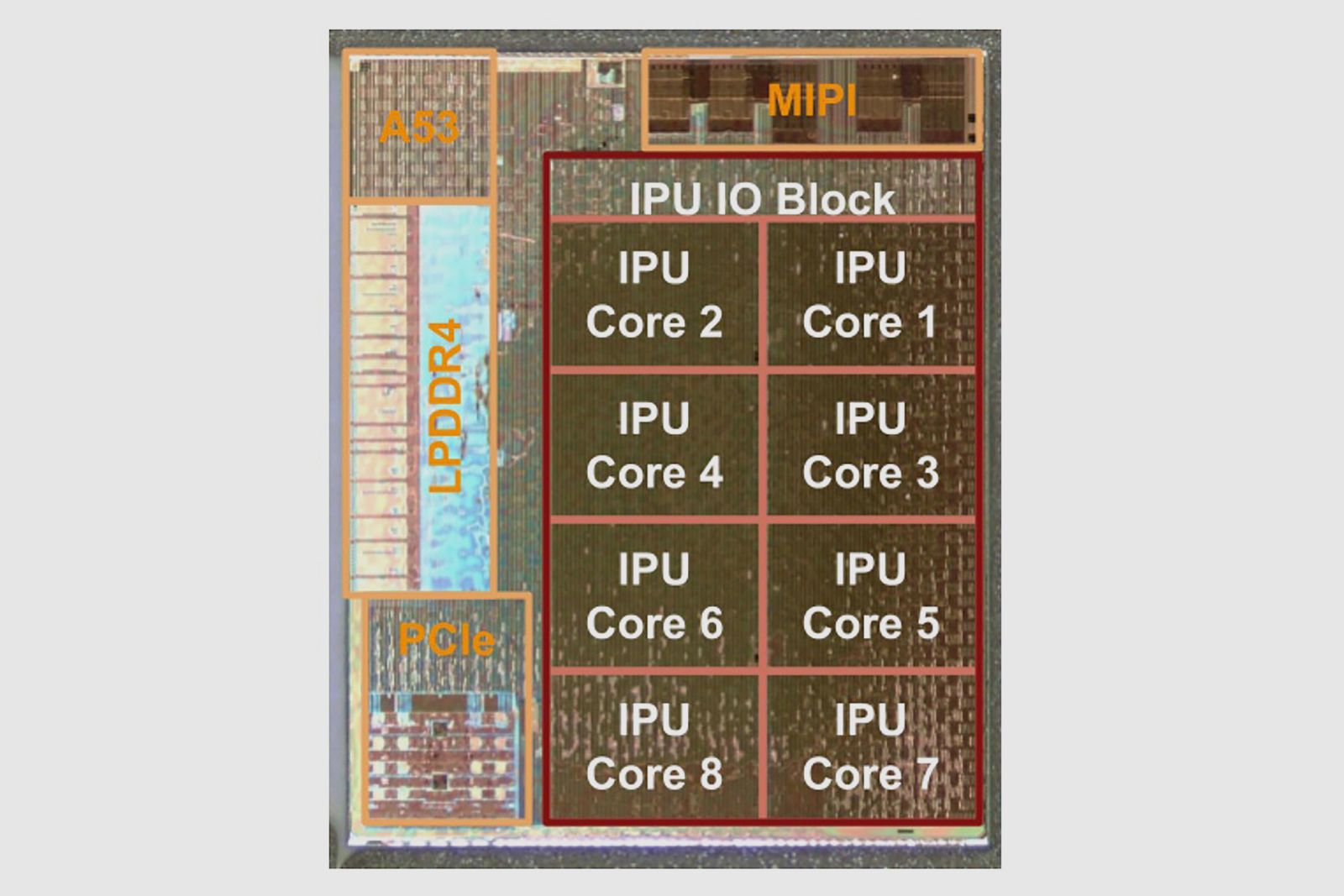
The Pixel phones are known for taking super shots, and the Pixel Visual Core - which has eight custom Image Processing Unit (IPU) cores as you can see below (each with 512 arithmetic logic units or ARUs). According to Google, this delivers raw performance of more than 3 trillion operations per second.
Google says "a key ingredient to the IPU’s efficiency" is the tight coupling of hardware and software because its self-designed software controls "many more details of the hardware" than in a typical processor. Controlling things through software means the hardware can be simpler and so more power efficient.
Like basically every other mobile chip out there, Pixel Core features some ARM design, with the Cortex-A53 chip that you can see in the top-left corner on the image above.
HDR (High Dynamic Range) enables you to capture balanced photos in situations where the photo is dim generally or where there are either both unduly bright and shaded areas which would have previously resulted in an unbalanced image.
Like the main Pixel camera, Pixel Visual Core also runs RAISR, which means zoomed-in shots look sharper and more detailed through machine learning.
Pixel Core is also designed to further reduce any possibility of shutter lag while Google also said last year that new uses for Pixel Visual Core will arrive over time, as it is programmable.
Liked this? Check out Google Pixel 2 and 2 XL tips and tricks